Flexor synergy patterns are crucial concepts in neurorehabilitation and motor control, particularly when discussing motor impairments resulting from neurological disorders such as stroke or traumatic brain injury. These patterns involve the coordinated movement of muscles in a specific sequence and are integral in both the assessment and treatment of motor dysfunction.
What is a Flexor Synergy Pattern?
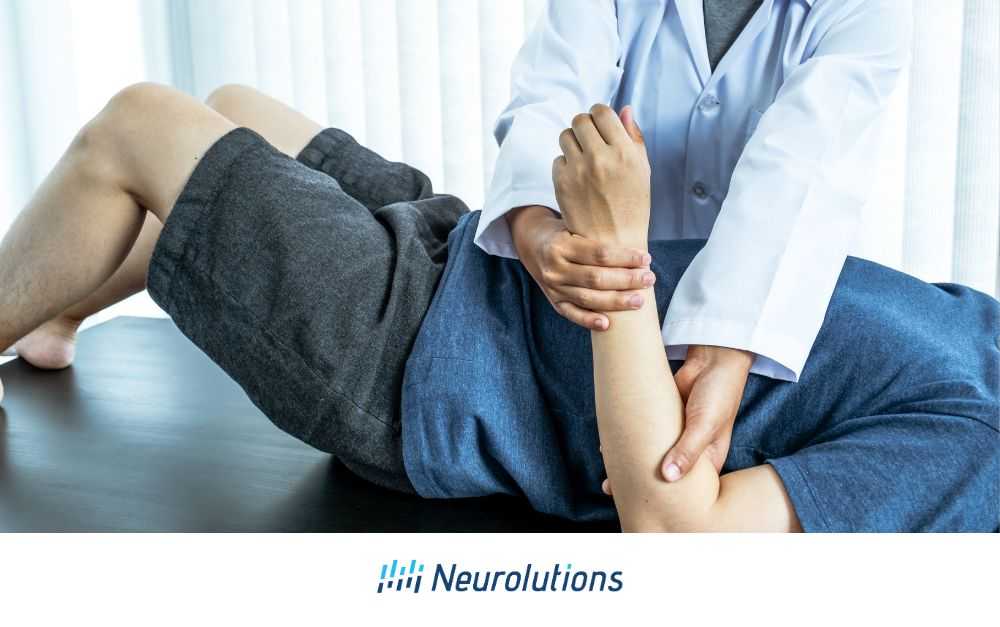
A flexor synergy pattern is a specific type of motor impairment where the activation of certain muscle groups occurs in a fixed, predictable pattern. This often happens when there is damage to the motor pathways in the brain or spinal cord. For instance, after a stroke, a common manifestation is the involuntary flexion of the arm at the elbow, wrist, and fingers, while the legs might show extension at the knee and hip.
In simpler terms, it means that when one part of the body moves, it tends to affect other parts in a set way. For example, if you move your arm, you might notice that your hand, wrist, and elbow move in a predetermined pattern that doesn’t allow for fine motor control. This can be particularly problematic for individuals trying to regain normal movement patterns after an injury or stroke.
Clinical Implications
Flexor synergy patterns have significant implications in both diagnosis and rehabilitation. Clinicians often use these patterns to assess the extent of motor impairment and to design appropriate rehabilitation strategies. The presence and severity of these patterns can help determine the type and intensity of therapy required.
- Assessment and Diagnosis: Flexor synergy patterns are assessed using various clinical tests and scales. For instance, the Brunnstrom Stages of Motor Recovery are commonly used to evaluate the presence of these patterns. In early stages, the patient may exhibit strong flexor synergy patterns, which can progressively diminish with effective rehabilitation.
- Rehabilitation Strategies: Rehabilitation often involves strategies to counteract or re-train these automatic patterns. Techniques such as constraint-induced movement therapy (CIMT) and task-specific training are used to help patients regain more functional movement patterns. For instance, CIMT involves restraining the unaffected limb to encourage the use of the affected one, which can help in breaking the dominant flexor synergy pattern and promoting more independent movements.
Mechanisms Behind Flexor Synergy Patterns
Understanding the mechanisms behind flexor synergy patterns requires knowledge of the motor control systems in the brain. The motor cortex, basal ganglia, and cerebellum all play roles in coordinating voluntary movement. When these systems are disrupted, as in the case of a stroke, the result can be abnormal patterns of movement, including flexor synergy patterns.
The underlying issue often involves an imbalance in neural control, where the excitatory and inhibitory signals required for smooth, coordinated movement are disrupted. This imbalance can lead to the overactivation of flexor muscles and underactivation of extensors, resulting in the characteristic patterns of movement seen in patients with motor impairments.
Implications for Daily Life
For individuals affected by flexor synergy patterns, daily life can be significantly impacted. Simple tasks such as dressing, eating, or writing can become challenging due to the inability to control movements effectively. The fixed patterns of movement can limit functional use of the affected limbs, leading to decreased independence and quality of life.
In daily activities, individuals may need to use adaptive strategies or assistive devices to manage these limitations. Occupational and physical therapists play a key role in helping patients adapt to these changes and work on regaining as much functionality as possible.
Future Directions
Research into flexor synergy patterns continues to evolve, with ongoing studies focusing on better understanding the underlying neural mechanisms and developing more effective treatments. Advances in neuroplasticity and rehabilitation techniques hold promise for improving outcomes for individuals with these motor impairments.
Emerging therapies, including robotics and virtual reality, offer new ways to engage patients in rehabilitation. These innovative approaches aim to break the rigid flexor synergy patterns and promote more natural movement patterns, ultimately improving functional outcomes and enhancing quality of life.
Diagnosis
Flexor synergy patterns are a significant aspect of motor impairment in neurological disorders, influencing both the assessment and treatment of these conditions. Understanding these patterns helps clinicians design effective rehabilitation strategies, while ongoing research continues to offer hope for improved treatments and better functional outcomes. As the field advances, the goal remains to help individuals regain as much independence and quality of life as possible, moving beyond the constraints of flexor synergy patterns.